What Is Amortization?
Another main difference is that amortization is nearly all the time applied utilizing the straight-line method, whereas depreciation can be applied utilizing both the straight-line or accelerated technique. Finally, as a result of they are intangible, amortized belongings don’t have a salvage worth, which is the estimated resale value of an asset at the end of its helpful life. An asset’s salvage value must be subtracted from its price to determine the quantity in which it can be depreciated.
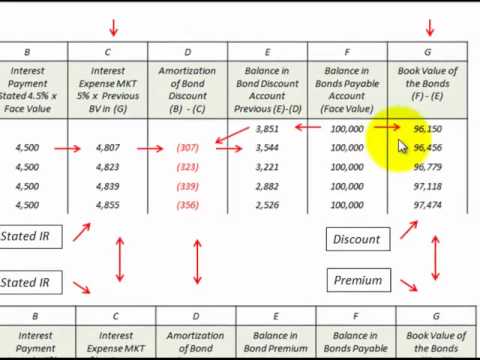
Amortization
For the purpose of accounting, a trademark is capitalized, that means that it’s recorded within the books of accounts as an asset by way of a journal entry. It isn’t widespread to report amassed amortization as a separate line item on the stability sheet.
The company’s accountants could also be challenged, nonetheless, when attempting to set the initial guide worth and amortizable life of intangible belongings. Ultimately, nonetheless, these value judgments inevitably include a subjective component. Amortization refers back to the accounting procedure that gradually reduces the guide value(carrying worth) of an intangible asset, over time, just as depreciation expenses cut back the book worth of tangible belongings. Asset amortization—like depreciation—is a non-cash expense that reduces reported income and thus creates tax savings for house owners. The length of time over which numerous intangible property are amortized vary extensively, from a few years to as many as forty years.
Goodwill in accounting is an intangible asset that arises when a purchaser acquires an current business. Goodwill also does not include contractual or different authorized rights regardless of whether or not these are transferable or separable from the entity or different rights and obligations. Goodwill is also only acquired by way of an acquisition; it cannot be self-created. Examples of identifiable assets which are goodwill include a company’s brand identify, buyer relationships, artistic intangible property, and any patents or proprietary expertise. The goodwill amounts to the surplus of the “buy consideration” (the money paid to purchase the asset or enterprise) over the net value of the belongings minus liabilities.
What is an example of amortization?
Amortization expense is the write-off of an intangible asset over its expected period of use, which reflects the consumption of the asset. The accumulated amortization account appears on the balance sheet as a contra account, and is paired with and positioned after the intangible assets line item.
More typical presentations are to incorporate accumulated amortization within the accrued depreciation line merchandise, or to current intangible belongings internet of accrued amortization on a single line item. The value of intangible property in private trade can be real and enormous (see the article Branding, for instance).
Amortization is an accounting method used to periodically decrease the e-book value of a loan or intangible asset over a set time period. First, amortization is used in the process of paying off debt via regular principal and curiosity funds over time. An amortization schedule is used to cut back the present stability on a loan, for example a mortgage or automobile mortgage, through installment funds. Second, amortization can even refer to the spreading out of capital bills related to intangible belongings over a specific period – often over the asset’s useful life – for accounting and tax purposes.
Amortization is a straightforward method to evenly unfold out costs over a time period. Typically, we amortize gadgets similar to loans, rent/mortgages, annual subscriptions and intangible belongings. In accounting, the amortization of intangible property refers to distributing the cost of an intangible asset over time. You pay installments utilizing a fixed amortization schedule all through a delegated interval.
And, you report the parts of the cost as amortization expenses in your books. Amortization reduces your taxable earnings all through an asset’s lifespan. Amortization is an accounting term that refers to the means of allocating the cost of an intangible asset over a time frame. The key distinction between amortization and depreciation is that amortization is used for intangible property, whereas depreciation is used for tangible assets.
What is the journal entry for amortization expense?
Amortization is the process of incrementally charging the cost of an asset to expense over its expected period of use, which shifts the asset from the balance sheet to the income statement. Examples of intangible assets are patents, copyrights, taxi licenses, and trademarks.
While a business can invest to extend its reputation, by promoting or assuring that its products are of top quality, such expenses can’t be capitalized and added to goodwill, which is technically an intangible asset. Goodwill and intangible assets are usually listed as separate gadgets on a company’s balance sheet. Amortization is a technique of spreading the price of an intangible asset over a particular time period, which is usually the course of its helpful life. Intangible belongings are non-physical assets that are nonetheless essential to a company, such as patents, logos, and copyrights. The objective in amortizing an asset is to match the expense of buying it with the revenue it generates.
- Goodwill is also solely acquired via an acquisition; it can’t be self-created.
- Goodwill in accounting is an intangible asset that arises when a buyer acquires an existing enterprise.
- Goodwill also doesn’t include contractual or different authorized rights no matter whether those are transferable or separable from the entity or different rights and obligations.
Intangibles are belongings like patents and licenses that are of great worth to a company and have an estimated helpful life. The value is amortized over the useful life to record bills within the interval they’re used. In 2001, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) declared in Statement 142, Accounting for Goodwill and Intangible Assets, that goodwill was now not permitted to be amortized. In accounting, goodwill is accrued when an entity pays more for an asset than its truthful worth, based mostly on the company’s model, client base, or different components.
Recording Amortization
Amortization is a common-sense accounting principle meant to replicate an financial actuality. Just as the advantage of long-time period items similar to intangible property lasts over a interval of years, the related expense of acquiring that asset should be spread out over the same amount of time.
Corporations use the purchase methodology of accounting, which doesn’t permit for computerized amortization of goodwill. Goodwill is carried as an asset and evaluated for impairment at least every year.
However, a rise within the fair market value wouldn’t be accounted for in the monetary statements. Private corporations in the United States, however, could elect to amortize goodwill over a interval of ten years or much less underneath an accounting various from the Private Company Council of the FASB. Amortization and depreciation are non-money bills on a company’s revenue statement. Depreciation represents the price of capital belongings on the balance sheet being used over time, and amortization is the same value of using intangible property like goodwill over time.
Amortization is the process of expensing the use of intangible assets over time versus recognizing the price solely in the year it is acquired. Many times when a business acquires something, the amount spent is immediately used to decrease earnings. When something is amortized, the acquisition price is split by the asset’s “useful life,” and that amount is used to lower a enterprise’ revenue over a period of years. Useful life is a time period that describes how long an asset can be used before it is depleted.
Accounting Entry to Amortize Intangible Assets

It is classed as an intangible asset on the steadiness sheet, since it could possibly neither be seen nor touched. Under US GAAP and IFRS, goodwill isn’t amortized, as a result of it’s considered to have an indefinite useful life. Instead, administration is responsible for valuing goodwill every year and to find out if an impairment is required. If the truthful market worth goes below historic value (what goodwill was bought for), an impairment should be recorded to convey it right down to its truthful market value.
What could be amortized?
Similarly, we create schedules and amortize for loans and different contracted liabilities. Amortization of an intangible asset is the equal to depreciating a tangible asset like equipment.