The Benefits to Investing in Bonds
A key threat of proudly owning mounted price bonds is interest rate threat or the chance that bond rates of interest will rise, making an investor’s current bonds less priceless. For example, let’s assume an investor purchases a bond that pays a set rate of 5%, but rates of interest within the economic system increase to 7%. This implies that new bonds are being issued at 7%, and the investor is no longer earning the best return on his funding as he might. Because there is an inverse relationship between bond prices and interest rates, the value of the investor’s bond will fall to replicate the higher interest rate out there. If he needs to promote his 5% bond to reinvest the proceeds within the new 7% bonds, he may accomplish that at a loss, as a result of the bond’s market value would have fallen.
Yield to Call (YTC)
What is Bond Interest Rate?
When a bond is issued, it pays a fixed rate of interest called a coupon rate until it matures. A bond’s interest rate is related to the current prevailing interest rates and the perceived risk of the issuer. Let’s say you have a 10-year, $5,000 bond with a coupon rate of 5%.
This can have a harmful effect on the common value of a bond fund, referred to as its web asset value (NAV). Hence, bond funds have an additional threat during periods of rising rates of interest, known as redemption risk. Redemption threat exaggerates the pain for those who remain within the fund. Bond funds work in another way than bonds because mutual funds include dozens or hundreds of holdings and bond fund managers are continuously shopping for and selling the underlying bonds held in the fund.
What Are the Risks of Investing in a Bond?
Generally, asset allocation models recommend that older or extra conservative traders keep the next proportion of their investments in money market funds or quick-time period bonds, versus shares. A widespread false impression amongst beginning traders is that “bond mutual funds are safe.” Investors can understandably confuse the time period “fixed income” with prices that do not fluctuate. However, fixed income investments, corresponding to bond mutual funds, can depreciate in value. The major investment purpose to buy a bond is for the income. Most bonds include a hard and fast interest rate, providing regular semi-annual payments to buyers.

How To Evaluate Bond Performance
Perhaps you’ve got heard the term, “The Fear Trade.” During periods of fear, many investors promote dangerous belongings and invest them in safer investments. This could be a unfavorable political or financial occasion, a natural disaster, a terrorist assault (or the threat of one), etc. This prompts buyers who own dangerous assets, corresponding to stocks, to promote. Treasuries that are thought-about to be one of the most secure investments on the planet. Because such a large amount of cash flows into these securities, it drives their worth up.
But individuals who purchase and sell bonds earlier than maturity are uncovered to many risks, most importantly changes in interest rates. When rates of interest enhance, the value of current bonds falls, since new points pay a better yield.
Risks of Bonds
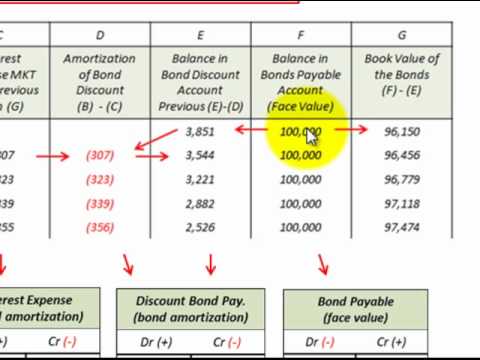
The major approach to default is to not pay in full or not pay on time. For example, a given bond fund will maintain tons of, perhaps several thousand individual bonds. When interest rates rise, to avoid further losses, shareholders in a bond fund will liquidate their shares. When this occurs, the fund manager could also be forced to sell bonds prematurely to be able to raise sufficient cash to satisfy its redemption requests.
- This could possibly be a unfavorable political or economic occasion, a natural disaster, a terrorist assault (or the specter of one), and so forth.
- This prompts traders who own dangerous belongings, corresponding to stocks, to sell.
- Perhaps you have heard the term, “The Fear Trade.” During durations of concern, many investors promote dangerous property and make investments them in safer investments.
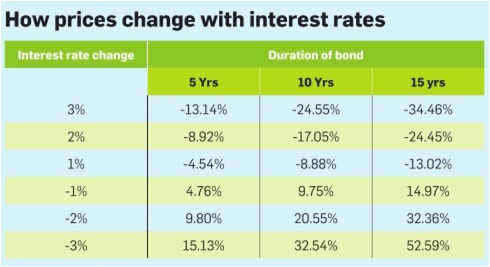
And, there are some steps you possibly can take to protect yourself from rising rates of interest. Furthermore, the longer the maturity, the larger the swing in price in relation to rate of interest movements. In a interval of rising rates and declining prices, the long-term bond funds will decline in worth more than intermediate-time period and short-term bonds. Therefore some traders and cash managers will shift their mounted earnings investments to shorter maturities when rates of interest are expected to rise. When rates of interest are declining longer maturities (i.e. lengthy-time period bond funds) is usually a better bet.
The longer the fixed rate bond’s term, the higher the risk that rates of interest would possibly rise and make the bond much less valuable. I am a CFP skilled with in depth expertise working with wealthy and prosperous shoppers. After 30 years, having worked with a few of the largest firms on the earth, I will try and carry the veil and take you behind the scenes of the monetary services industry. I will focus on the universe of investments together with mutual funds, ETFs, bonds, and shares. In addition, I will present you, the reader, with sensible, useable info, to empower you to take charge of your financial life, bringing readability to the complicated.
An important part of the bond market is the federal government bond market, due to its dimension and liquidity. Government bonds are sometimes used to compare other bonds to measure credit danger. The yield on government bonds in low danger countries such because the United States or Germany is thought to point a threat-free price of default.
As mentioned here previously, bond funds wouldn’t have a “worth” but quite a Net Asset Value (NAV) of the underlying holdings. Managers also have to fulfill redemptions (from other investors withdrawing money from the mutual fund).
Bond Ratings
Likewise, when rates of interest decrease, the value of present bonds rises, since new issues pay a lower yield. This is the fundamental concept of bond market volatility—modifications in bond costs are inverse to changes in rates of interest. Fluctuating rates of interest are part of a country’s monetary policy and bond market volatility is a response to anticipated monetary policy and economic adjustments. While many investments provide some type of revenue, bonds have a tendency to offer the very best and most reliable cash streams.
Diversification is all about investing in different types of belongings to decrease the overall danger of your portfolio. Bonds play an essential role in most asset allocation models, which divide investments amongst shares, cash market funds and other forms of investments. Since bonds typically fluctuate in value less than shares, they will easy out the swings in your portfolio and dampen your general danger.
This provides predictability of each money circulate and return, one thing that different investments, similar to shares, cannot offer. For example, if you buy a $1,000 bond that pays 5 p.c interest, you’ll obtain $25 twice per 12 months for so long as you own the bond. You may even obtain your $1,000 back on the finish of the bond’s life, known as the maturity date. In basic, the bond market is risky, and stuck revenue securities carry interest rate risk. (As rates of interest rise, bond prices often fall, and vice versa. This impact is normally extra pronounced for longer-time period securities).
The actual value of a hard and fast fee bond is susceptible to loss as a result of inflation. Because the bonds are lengthy-term securities, rising costs over time can erode the buying power of every curiosity fee a bond makes. For example, if a ten-yr bond pays $250 fastened coupons semi-yearly, in five years, the true value of the $250 will be nugatory right now. When investors fear that a bond’s yield gained’t sustain with the rising costs of inflation, the value of the bond drops because there may be much less investor demand for it.
Basic Bond Characteristics
When it comes to bonds, prices and yields move in the other way. Hence, when worry rises and cash flows into bonds, it pushes prices greater and yields decrease.
Fixed earnings securities additionally carry inflation risk, liquidity threat, call threat and credit and default risks for each issuers and counterparties. Lower-high quality fastened earnings securities contain greater danger of default or worth modifications due to potential changes in the credit high quality of the issuer. Foreign investments contain greater risks than U.S. investments, and can decline considerably in response to antagonistic issuer, political, regulatory, market, and economic risks. Any fixed-earnings safety offered or redeemed previous to maturity may be subject to loss.
Therefore, when rates of interest rise, bond costs fall, and bond buyers, especially those who stay in bond funds, will feel some degree of ache. However, to put this in its proper context, when bonds lose value, it is usually not as dangerous as a decline within the inventory market.