
Should financial leverage be high or low?
This ratio, which equals operating income divided by interest expenses, showcases the company’s ability to make interest payments. Generally, a ratio of 3.0 or higher is desirable, although this varies from industry to industry.When shareholders own a majority of the assets, the company is said to be less leveraged. When creditors own a majority of the assets, the company is considered highly leveraged.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Debt Financing For Working Capital?
In finance, leverage refers to using borrowed capital or financial derivatives to magnify the results of an investment. Analyze the potential changes in the costs of leverage of your investments, in particular an eventual increase in interest rates. The paper fills two major gaps in the theory and practice of corporate finance. Although research in real options has been underway for well over 30 years, the literature has been silent on whether and how to incorporate taxes and debt capacity in real-option valuation. As a result, textbook treatments of two closely related topics—the valuation of real options and the valuation of assets in place—have been disconnected. The Critical Finance Review has published “Real Options, Taxes and Financial Leverage” by Brattle Principals Stewart Myers and James Read.But the shares of commercial and industrial (C&I), CRE, and residential mortgage loans in loss mitigation have remained elevated. The leverage of firms with existing C&I loans from the largest banks declined during the second half of 2020, though it stayed somewhat elevated relative to historical levels (figure 3-3). Over the same period, delinquency rates remained about unchanged for most types of loans but rose for CRE loans secured by COVID-affected properties, such as hotels and retail properties. Thus, the prospects of financial leverage help the finance manager to make an appropriate decision by comparing the cost of debt financing with the average return on investment. Companies practice financial leverage when they use debt capital to purchase assets. While taking on debt means that a company will need to pay interest expenses, the assets acquired using that debt financing are expected to earn an amount of money greater than that interest expense.Whether a company is leveraging too much is dependent on several factors, including the industry and age of the company. The most obvious indicator of too much leverage is an inability to pay off debts. If a company defaults on its lending agreements, it has leveraged too much debt.
What do the terms financial leverage and financial risk mean?
Financial risk relates to how a company uses its financial leverage and manages its debt load. Business risk relates to whether a company can make enough in sales and revenue to cover its expenses and turn a profit. With financial risk, there is a concern that a company may default on its debt payments.You can assess how debt is contributing to earnings by the degree of financial leverage, which shows how much earnings per share, or EPS, will increase because of increased debt. When your business takes on debt, you create conflicting forces on EPS. On the plus side, the debt helps to grow the company by paying for new profitable projects and investments — this increases earnings without increasing the number of shares, so EPS rises.
Financial Leverage And The Lehman Brothers Collapse
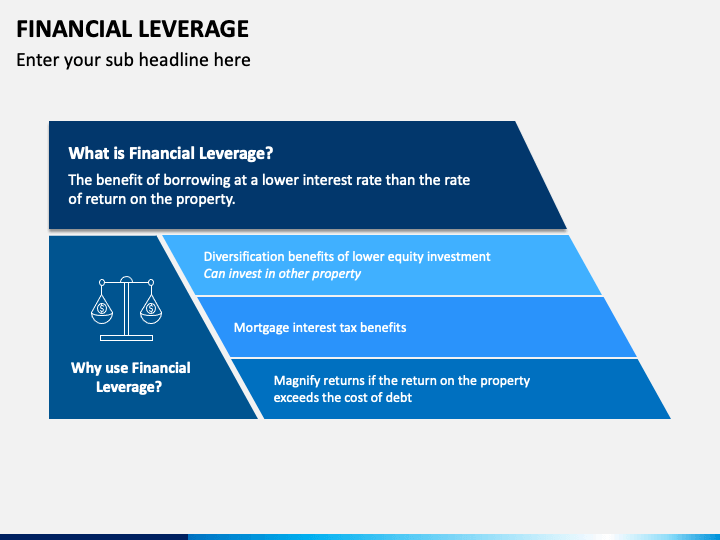
If the financial leverage is positive, the finance manager can go for increasing the debt to enhance benefits to shareholders. Where the earning is either equal to fixed financial charge or unfavorable, debt financing should not be encouraged.
Financial leverage is measured using leverage ratios and a company’s financial data found on its balance sheet, cash flow statement, or income statement. You can measure how much of a company’s capital structure and working capital (capital a business uses in its day-to-day operations) are made up of debt using these ratio formulas. In other words, the financial leverage ratios measure the overall debt load of a company and compare it with the assets or equity. This shows how much of the company assets belong to the shareholders rather than creditors.
Example Of Financial Leverage
This makes leveraged ETFs a lower risk approach to leveraged investing. If the value of your shares fall, your broker may make a margin call and require you to deposit more money or securities into your account to meet its minimum equity requirement.Similarly, one could calculate the degree of operating leverage by dividing a company’s EBIT by EBIT less interest expense. A higher degree of operating leverage shows a higher level of volatility in a company’s EPS.One can calculate the equity multiplier by dividing a firm’s total assets by its total equity. Once figured, one multiplies the financial leverage with the total asset turnover and the profit margin to produce the return on equity. For example, if a publicly traded company has total assets valued at $500 million and shareholder equity valued at $250 million, then the equity multiplier is 2.0 ($500 million / $250 million). Should a business increase or reduce the number of units it is producing?For many businesses, borrowing money can be more advantageous than using equity or selling assets to finance transactions. When a business uses leverage—by issuing bonds or taking out loans—there’s no need to give up ownership stakes in the company, as there is when a company takes on new investors or issues morestock. Leverage can be used to help finance anything from a home purchase to stock market speculation. Businesses widely use leverage to fund their growth, families apply leverage—in the form of mortgage debt—to purchase homes, and financial professionals use leverage to boost their investing strategies. Baker Company uses $100,000 of its own cash and a loan of $900,000 to buy a similar factory, which also generates a $150,000 annual profit. Baker is using financial leverage to generate a profit of $150,000 on a cash investment of $100,000, which is a 150% return on its investment.The consumer leverage ratio is used to quantify the amount of debt the average American consumer has relative to theirdisposable income. Tim Nuding, CFA is the Chief Executive of Prosperity Capital Services LLP, a firm that provides research and consulting services for alternative investments. Tim is also the Founder of the Hedge Fund Research Club, sponsored by the CFA Society of the UK and CAIA London chapter. Tim formerly managed international asset management and investment banking businesses for Citibank and Dresdner Bank in the UK and Japan. He received his CFA charter in 2000 and is active in the CFA Society of the UK and the CFA Institute. Immediately, we can see that the level of interest to be paid is critical to the leverage proposition.
- If you want profitable assets, you’re gonna have to risk leveraging some amount of debt.
- The unusually large swings in profits caused by a large amount of leverage increase the volatility of a company’s stock price.
- Common leverage ratios include the debt-equity ratio, equity multiplier, degree of financial leverage, and consumer leverage ratio.
- They measure the ability of the business to meet its long-term debt obligations, such as interest payments on debt, the final principal payment on the debt, and any other fixed obligations like lease payments.
- Businesses widely use leverage to fund their growth, families apply leverage—in the form of mortgage debt—to purchase homes, and financial professionals use leverage to boost their investing strategies.
Instead of paying for the building in cash, you decide to use $200,000 of your own money, borrowing the additional $400,000 needed. While financial leverage can be profitable, too much financial leverage risk can prove to be detrimental to your business. Always keep potential risk in mind when deciding how much financial leverage should be used. Option B allows Joe to use $100,000 of his own money and borrow an additional $650,000 from the bank in order to purchase a much bigger building. If Joe borrows from the bank, he will also have to pay 5% interest on the loan. While not always the best option for small businesses, financial leverage can be beneficial.
How Much Leverage Is Too Much?
However, if it merely creates goods purchases for current consumption, then it is “bad” leverage. A renowned but less-quoted economist of the 20th century, Hyman Minsky, distinguished between three types of debt. In the first and ideal type of debt, loans would be paid back with profits from purchased assets (“hedge financing”). In the second type of debt, profits from the asset purchased merely paid the interest on the debt (“speculative finance”). In the third type of debt, the asset being financed was required to be sold at ever higher prices in order to sustain profitability (“Ponzi finance”). Minsky suggested in his financial instability hypothesis that capitalist economies tended to move from hedge finance to speculative and Ponzi finance over prolonged periods of prosperity. The next point to note is that many tax regimes create an incentive in favor of leverage by making interest paid tax deductible — again, creating a somewhat unhealthy bias toward increasing debt levels.

Financial leverage is a strategy where your company uses Debt to acquire assets. When you get financing, you have much more buying power and can purchase equipment or real estate that might be otherwise impossible for you to do. A few recent episodes have highlighted the opacity of risky exposures and the need for greater transparency at hedge funds and other leveraged financial entities that can transmit stress to the financial system. Life insurers invest heavily in corporate bonds and hold CLOs, which leaves them vulnerable to risks from elevated leverage in the corporate sector. If the performance of their debt holdings deteriorates, life insurers’ capital positions could be impaired.With very low interest rates, many more investments meet the expected minimum hurdle of returning the interest paid and vice versa. Some would even say that ultra-low interest rates create an unhealthy misallocation of capital resources (i.e., inducing investors to make investments that have insufficient returns over the long term). Due to the interest expense, EBT is lower for L in comparison with U and therefore, the ratio EBIT/EBT is greater.Leverage is an investment strategy of using borrowed money—specifically, the use of various financial instruments or borrowed capital—to increase the potential return of an investment. The idea is to borrow funds and then to invest those funds at a rate of return that exceeds theinterest rateon the loan. If the investor is able to borrow money at 5%, and then invest it at 7%, that investor can pocket the difference. And if such an opportunity exists, the investor would want to lever up as much as possible – that is, borrow as much money as possible at 5% to invest at 7%. John Mauldin, the investment author and commentator, drives home the point that the problem of slow economic growth is not because of the lack of consumption but because of the lack of income. All else being equal, increased productivity increases income for labour and capital.
How Is Ebit Breakeven Affected By Leverage And Financing Plans?
Even if cash flows and profits are sufficient to maintain the ongoing borrowing costs, loans may be called-in. Normally, the lender will set a limit on how much risk it is prepared to take and will set a limit on how much leverage it will permit, and would require the acquired asset to be provided as collateral security for the loan.

It used a hodge-podge menu of about $150 billion in short- and long-term debt, and $180 billion in repurchase, or “repo” agreements as collateral on short-term, repo loans. Once investors began doubting the quality of the collateral Lehman was using, they largely stopped allowing the company to roll over the repo loans into the next 24-hour period, and began asking for their money back – in full.From an after-tax cash flow perspective, the government is, in effect, subsidizing a portion of the interest expense. Just know going in that accompanying costs can escalate, the economics of financial leverage can be exceedingly complex, and financing risks can be higher for companies using financial leverage. There is no guarantee that financial leverage will produce a positive outcome. Basically, the higher the amount of debt a company uses as leverage, the higher – and the riskier – is its financial leverage position. Debt-to-capital ratios are often used by investors to determine risk when investing in a company. These ratios are calculated by dividing a company’s total Debt by a company’s total capital. Generally, the lower the ratio, the easier it is for your company to secure better business loan options and investments.For instance, if your business borrows $50,000 from the bank to purchase additional inventory for resale, that is using financial leverage. Let’s understand the effect of leverage with the help of the following example. The calculation below clearly shows the effect of having debt in the capital. The return on equity and the EPS both are higher in the case of debt and equity structure.A year before its demise, Lehman’s leverage ratio was a massive 30-to-1. The company had $22 billion in equity to back $691 billion in total assets. At that point, even a minuscule drop in asset value of 3% was enough to send one of Wall Street’s giants careening into oblivion. A business steers $5 million to purchase a choice piece of real estate to build a new manufacturing plant.
Understanding Leverage
In other words, after all of the liabilities are paid off, how much of the remaining assets the investors will end up with. The equity ratio also measures how much of a firm’s assets were financed by investors, or the investors’ stake in the company. Operating leverage is a measure of the number of fixed costs of the company such as rent and office salaries and so on.This can be a problem when accounting for stock options issued to employees, since highly volatile stocks are considered to be more valuable, and so create a higher compensation expense than would less volatile shares. Sue uses $500,000 of her cash and borrows $1,000,000 to purchase 120 acres of land having a total cost of $1,500,000. Sue is using financial leverage to own/control $1,500,000 of property with only $500,000 of her own money. Let’s also assume that the interest on Sue’s loan is $50,000 per year and it is paid at the beginning of each year. In corporate finance, the debt-service coverage ratio is a measurement of the cash flow available to pay current debt obligations. Times interest earned , also known as a fixed-charge coverage ratio, is a variation of the interest coverage ratio. This leverage ratio attempts to highlight cash flow relative to interest owed on long-term liabilities.