- An investment in the fund is not insured or guaranteed by the FDIC or any other government agency.
- Any company we affiliate with has been fully reviewed and selected for their quality of service or product.
- Subtract what you paid last year against the total amount you owed to derive the amount of money due.
- Every time a sale or expense is recorded, affecting the income statement, the assets or liabilities are affected on the balance sheet.
- Service-based companies, like hair salons or law firms, sell services, not goods to customers, so they do not typically have inventory or raw products on the balance sheet.
- The current ratio, quick ratio and working capital are all measures of a company’s liquidity.
While these assets are not physical in nature, they are often the resources that can make or break a company—the value of a brand name, for instance, should not be underestimated. Lastly, balance sheet example inventory represents the company’s raw materials, work-in-progress goods and finished goods. Depending on the company, the exact makeup of the inventory account will differ.One is called a cash flow statement which helps track cash inflow and outflow), but honestly it’s complicated and I know very few people who do this for their personal finances. Verify that the total for all assets shown in the balance sheet equals the total for all liability and stockholders’ equity accounts. Net Worth – The business owner’s equity in a company as represented by the difference between assets and liabilities. Now that you have created a balance sheet for your business, there are some easy calculations that you can perform that will give you a better understanding of your company. Using data from your balance sheet, you can calculate liquidity and leverage ratios. Long-term liabilities are any debts that must be repaid by your business more than 1 year from the date of the balance sheet. This may include startup financing from relatives, banks, finance companies or others.An asset’s initial book value is its its acquisition cost or the sum of allowable costs expended to put it into use. In many cases, the carrying value of an asset and its market value will differ greatly. If the asset is valued on the balance at market value, then its book value is equal to the market value. Cash, receivables, and liabilities are re-measured into U.S. dollars using the current exchange rate.
Assets = Liabilities + Owners Equity
Financial strength ratios, such as the working capital and debt-to-equity ratios, provide information on how well the company can meet its obligations and how the obligations are leveraged. On the balance sheet, you can see how assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity are reported.
What is balance sheet with example?
The balance sheet displays the company’s total assets and how the assets are financed, either through either debt or equity. It can also be referred to as a statement of net worth or a statement of financial position. The balance sheet is based on the fundamental equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.The general ledge will indicate the current value of long-term assets. The balance sheet is created to show the assets, liabilities, and equity of a company on a specific day of the year. As you can see, the report form presents the assets at the top of the balance sheet.This account includes the balance of all sales revenue still on credit, net of any allowances for doubtful accounts . As companies recover accounts receivables, this account decreases, and cash increases by the same amount. Balance sheets, like all financial statements, will have minor differences between organizations and industries. However, there are several “buckets” and line items that are almost always included in common balance sheets. We briefly go through commonly found line items under Current Assets, Long-Term Assets, Current Liabilities, Long-term Liabilities, and Equity. Liquidity ratios are a class of financial metrics used to determine a debtor’s ability to pay off current debt obligations without raising external capital. The main types of ratios that use information from a balance sheet are financial strength ratios and activity ratios.
Sample Balance Sheet
In addition, it shows the ratio of current assets and current liability, enabling a business to determine if it has the capability to pay its debts within a period of time. Assets, liabilities and ownership equity are listed as of a specific date, such as the end of its financial year. A balance sheet is often described as a “snapshot of a company’s financial condition. ” Of the four basic financial statements, the balance sheet is the only statement which applies to a single point in time of a business’ calendar year. There are three primary limitations to balance sheets, including the fact that they are recorded at historical cost, the use of estimates, and the omission of valuable things, such as intelligence. The current liabilities of most small businesses include accounts payable, notes payable to banks, and accrued payroll taxes. Accounts payable is the amount you may owe any suppliers or other creditors for services or goods that you have received but not yet paid for.
This financial statement details your assets, liabilities and equity, as of a particular date. Although a balance sheet can coincide with any date, it is usually prepared at the end of a reporting period, such as a month, quarter or year. Financial ratio analysis uses formulas to gain insight into a company and its operations. For a balance sheet, using financial ratios (like the debt-to-equity ratio) can provide a good sense of the company’s financial condition, along with its operational efficiency. It is important to note that some ratios will need information from more than one financial statement, such as from the balance sheet and the income statement. A balance sheet is an accounting report that provides a summary of a company’s financial health for a specified period.
Owner’s Equity
To ensure the balance sheet is balanced, it will be necessary to compare total assets against total liabilities plus equity. To do this, you’ll need to add liabilities and shareholders’ equity together.This can be compared with current assets such as cash or bank accounts, which are described as liquid assets. The balance sheet, like the cash flow statement and the income statement, are all required by GAAP rules. So, what is the difference between reporting from the balance sheet vs. income statement?In the investor’s income statement, the proportional share of the investee’s net income or net loss is reported as a single-line item. Financial statement analysis consists of applying analytical tools and techniques to financial statements and other relevant data to obtain useful information. This information reveals significant relationships between data and trends in those data that assess the company’s past performance and current financial position. The information shows the results or consequences of prior management decisions. In addition, analysts use the information to make predictions that may have a direct effect on decisions made by users of financial statements. Long-term liabilities are obligations that will not be paid off in the coming year.This could be the reporting period before, or the year before, your current balance sheet. These comparisons allow you to see how your finances are changing over time.It is important to remember that original cost may be more than the asset’s invoice price. It can include shipping, installation, and any associated expenses necessary for readying the asset for service. Assets are arranged in order of how quickly they can be turned into cash. Like the other fixed assets on the balance sheet, machineryand equipment will be valued at the original cost minus depreciation. Other assets are generally intangible assets such as patents, royalty arrangements, and copyrights.Along with fixed assets, such as plant and equipment, working capital is considered a part of operating capital. Investments accounted for by using the equity method are 20-50% stake investments in other companies. The investor keeps such equities as an asset on the balance sheet. The investor’s proportional share of the associate company’s net income increases the investment , and proportional payment of dividends decreases it.
What Does A Balance Sheet Look Like?
Balance sheets are one of the most critical financial statements, offering a quick snapshot of the financial health of a company. Learning how to generate them and troubleshoot issues when they don’t balance can help you become an invaluable member of your organization. Here are the steps you can follow to create a basic balance sheet for your organization. As with assets, liabilities can be classified as either current liabilities or non-current liabilities. A company’s balance sheet is one of the most important financial statements it will produce—typically on a quarterly or even monthly basis . Small Biz Ahead is a small business information blog site from The Hartford. We may receive compensation from companies we endorse on our blog.

Both current and non-current liabilities are included in the liabilities section of the balance sheet. Accessing balance sheet and income statement software is a surefire way to save you time, stress, and money — as you make the right decisions towards letting your business be the best that it can be. Every time a sale or expense is recorded, affecting the income statement, the assets or liabilities are affected on the balance sheet. When a business records a sale, its assets will increase or its liabilities will decrease. When a business records an expense, its assets will decrease or its liabilities will increase. The assets on the left will equal the liabilities and equity on the right. When reviewing a balance sheet, the two columns will reflect the balance sheet equation with line-item accounts showing how the two sides add up.
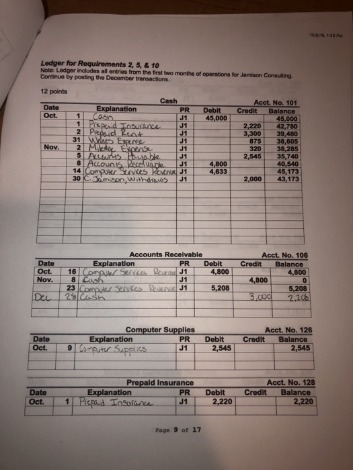
Balance Sheet
Current assets are assets that can turn into cash within one year of the balance sheet date. They are listed in order of relative liquidity, in other words how easily they could be converted into cash. The line items towards the top of the assets section are the most liquid, meaning those assets can be converted to cash the fastest. Use your spreadsheet software to create the form or shell for your balance sheet. Type in the name of your company and center it at the top of your balance sheet. Type in “Balance Sheet” on the second line, then enter the year for which you are reporting your information. Create separate sections for assets, investments and property and equipment on the left side of your spreadsheet.

If you are a manufacturing firm, this could be your largest fixed asset. Like the other fixed assets on the balance sheet, machinery and equipment will be valued at the original cost minus depreciation. They are distinguished from current assets by their longevity. Many small businesses may not own a large amount of fixed assets.
Determine The Time Period You’re Reporting On
Adding other financial statements to your small business “to-do” list may seem daunting. However, your financial documents can have important interactions and even feed off each other. For instance, your income statement will be linked with your balance sheet, despite providing different financial views of your small business. The trial balance is comprised of accounts for revenue, expenses, gains, losses, assets, liabilities, and equity. Eliminate from the trial balance all accounts except those for assets, liabilities, and equity. Incidentally, the eliminated accounts are used to construct the income statement.Enter any wages you owed at the end of the year under “wages payable” on the balance sheet. Use Schedule C to figure the exact amount you owed in wages at year’s end.Net income is the final calculation included on the income statement, showing how much profit or loss the business generated during the reporting period. Once you’ve prepared your income statement, you can use the net income figure to start creating your balance sheet. Your balance sheet will be separated into two main sections, cash and cash equivalent assets on the one side, and liabilities and equity on the other.