
Double-entry bookkeeping is an accounting system in which all financial transactions are recorded in two types of accounts, debits and credits. When you post a transaction, the number of debits and credits used can be different, but the total dollar amount of debits must equal credits. You may notice that these are the same terms you’ll see on an income statement, or P&L statement. Keep in mind that the goal of making all these journal entries is to produce accurate financial statements at the end of the accounting period.
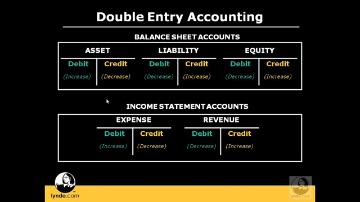
Income accounts represent the various types of monies received from different sources, such as interest or investment income or revenue gained from the sale of goods or services. Double-entry bookkeeping has been in use for at least hundreds, if not thousands, of years. Accounting has played a fundamental role in business, and thus in society, for centuries due to the necessity of recording transactions between parties. The main purpose of a double-entry bookkeeping system is to ensure that a company’s accounts remain balanced and can be used to depict an accurate picture of the company’s current financial position. A graphical view of the relationship between the 5 basic accounts.
In this case, assets (+$10,000 in inventory) and liabilities (+$10,000) are both affected. Both sides of the equation increase by $10,000, and the equation remains balanced. Accountants call this the accounting equation, and it’s the foundation of double-entry accounting. If at any point this equation is out of balance, that means the bookkeeper has made a mistake somewhere along the way. Reconciliation is an accounting process that compares two sets of records to check that figures are correct, and can be used for personal or business reconciliations. David Kindness is a Certified Public Accountant and an expert in the fields of financial accounting, corporate and individual tax planning and preparation, and investing and retirement planning. David has helped thousands of clients improve their accounting and financial systems, create budgets, and minimize their taxes.
Public companies have to follow any rules and methods outlined by GAAP. Record credits and debits for each transaction that occurs. With double-entry in accounting, record two or more entries for every transaction. Your general ledger is a record that sorts and summarizes your business transactions. You can use your general ledger to see where money is coming from and where it is going. With a general ledger, you can also see the amount of cash you have on hand and how much debt your business has.
Difference Between Single Entry And Double Entry Bookkeeping
Recording transactions and keeping financial records are an essential part of owning a business. One way you can keep track of your finances is by using double-entry accounting. Read on to learn what is double-entry accounting and how it can benefit your books.
It is actually similar to keeping your own personal checkbook. You keep a record of transactions like cash, tax-deductible expenses, and taxable income when you use single-entry bookkeeping. However, businesses have to keep a detailed accounting of their financial transactions. The survival of the business depends on the owner’s ability to establish good accounting practices. Accounting software can speed up the process immensely—to a point. Software can recognize patterns very well, meaning it can classify most transactions pretty easily, taking much of the everyday work of making debit and credit entries off your plate. The simplest way to understand it is to know that some accounts usually carry a credit balance and others carry a debit balance.
The closest example of this basic accounting is the bank account ledger you use to keep track of your spending. Because the accounts are set up to check each transaction to be sure it balances out, errors will be flagged to accountants quickly, before the error produces subsequent errors in a domino effect.
They ARE opposites because Accounts Payable is a liability account. An increase in a liability account means that what you owe to others is increasing, making your actual worth decrease. This entry tells you that you have increased shipping supplies by 2,500, and you’ve also increased your accounts payable balance by 2,500. If the customer did not pay cash but instead was extended credit, then “accounts receivable” would have been used instead of “cash.” Double-entry bookkeeping spread throughout Europe and became the foundation of modern accounting. The rules and guidelines for accounting are centuries old, and they’re complex. We’re setting out to change that so that business owners don’t need the help of accountants to decode their own finances.
Therefore, the combined debit balance of all accounts always equals the combined credit balance of all accounts. An example of a double-entry transaction would be if the company wants to pay off a creditor. The cash account would be reduced by the amount the company owes the creditor. Then, the double-entry reduces the amount the business now owes to the creditor account as it has received the amount of the credit the business is extending.
It can be used by companies to track transactions that involve cash, taxable income, and tax deductible expenses. Like the name suggests, income and expenses are only listed one time in a single row, with positive values for income and negative values for expenses. Equity is the owner’s stake, including owner contributions into the company. Imagine, for example, that you sold all of your assets for cash and used the cash to pay off all your liabilities. Now that we have talked about the double entry bookkeeping system, let’s move on to recording journal entries.
Company
Debits and credits each increase certain types of accounts and decrease others as described in the previous section. In asset and expense accounts, debits increase the balance and credits decrease the balance. In liability, equity and income accounts, credits increase the balance and debits decrease the balance. Double-entry bookkeeping is a method of recording transactions where for every business transaction, an entry is recorded in at least two accounts as a debit or credit. In a double-entry system, the amounts recorded as debits must be equal to the amounts recorded as credits.
For example, you might use Petty Cash, Payroll Expense, and Inventory accounts to further organize your accounting records. Dummies has always stood for taking on complex concepts and making them easy to understand. Dummies helps everyone be more knowledgeable and confident in applying what they know.
- A debit is an entry made on the left side of an account while a credit is an entry on the right side.
- Since the supplies were purchased with cash, your assets will decrease, so the same transaction is posted as a credit on the right side of the T-account.
- The entry is a debit of $4,000 to the fixed assets account and a credit of $4,000 to the cash account.
- With the single-entry system, you record cash disbursements and cash receipts.
- Read our comprehensive accounting reviews to learn more about these programs and find other great double-entry options.
- It’s easy to get hung up on the rules of double-entry accounting, but you can get past that by recognizing that it has a push-and-pull nature.
Double-entry accounting is a lot like learning multiplication. Understanding how to do it will equip you for all sorts of business challenges, specifically like how to read your financial statements with confidence and make thoughtful financial decisions. But just like there’s little benefit to knowing what 456 x 1,920 equals off the top of your head, there’s little benefit to knowing every last rule to double-entry bookkeeping. This is a debit to the wage account and a credit to the cash account. This means that you are consuming the cash asset by paying employees. Today, most accounting jobs have access to reputable accounting software has the double-entry method built in. Still, it’s a good idea to have a basic understanding of this critical accounting concept.
Software Features
In double-entry accounting, each transaction affectsat least two accounts. As you can imagine, if you have a transaction that affects a dozen accounts, it can be really hard to keep track of it all in a long algebra equation.
A compound entry is necessary when a single transaction affects three or more accounts. Suppose the company’s owner purchases a used delivery truck for $20,000 on August 6 by making a $2,000 cash down payment and obtaining a three‐year note payable for the remaining $18,000. This transaction is recorded by debiting the vehicles account for $20,000, crediting the notes payable account for $18,000, and crediting the cash account for $2,000. When finance professionals began writing down transactions, they’d have several different books, known as ledgers.
Expense accounts detail numbers related to money spent on advertising, payroll costs, administrative expenses, or rent. The modern double-entry bookkeeping system can be attributed to the 13th and 14th centuries when it started to become widely used by Italian merchants. Double entry refers to a system of bookkeeping that is one of the most important foundational concepts in accounting. AccuracySome error-checking is built in because debits must equal credits.
Bookkeeping For Your Small Business
He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
To prevent this from happening, you should complete a process called account reconciliation on a regular basis to keep your books accurate. That means you match every transaction in your accounting software to its corresponding bank statement. Double-entry accounting is a system that requires two book entries — one debit and one credit — for every transaction within a business. Your books are balanced when the sum of each debit and its corresponding credit equals double entry accounting zero. Contrary to single-entry accounting, which tracks only revenue and expenses, double-entry accounting tracks assets, liabilities and equity, too. For instance, if a business takes a loan from a financial entity like a bank, the borrowed money will raise the company’s assets and the loan liability will also rise by an equivalent amount. If a business buys raw material by paying cash, it will lead to an increase in the inventory while reducing cash capital .
Debits And Credits
The rating of this company or service is based on the author’s expert opinion and analysis of the product, and assessed and seconded by another subject matter expert on staff before publication. Merchant Maverick’s ratings are not influenced by affiliate partnerships. Double-entry will better reflect the reality of the business. But supposing that you have no fixed assets, that you pay every bill the day you receive it, and that you get paid for all work the day you invoice it, then single-entry should do you just fine. The one thing to keep in mind is that if you ever scale your business up, you’ll want to shift to a new accounting model along with it. Almost all of the accounting software reviews on our site feature double-entry accounting.
What is meant by zero balance in ledger?
A zero-balance account refers to a savings bank account, which has a zero balance in it and yet not charged. … Zero-balance accounts usually allow a limited number of transactions per month, usually around four. If the limit exceeds, then the bank will convert your zero-balance account into a regular savings account.
You use Modern Treasury to move funds between customer accounts you operate on behalf of your customers. Customers 1-3 buy and sell bagels to each other, and cash out the balances of their accounts on your platform to external banks. So, if assets increase, liabilities must also increase so that both sides of the equation balance.
Want More Helpful Articles About Running A Business?
Double-entry bookkeeping is an accounting system that rules that for every entry into one account, an equal entry must be made in another account. Said to date back to the 11th century, double-entry bookkeeping maintains that there must be an equal debit for every credit a company records in its accounting system. These transactions are recorded in a company’s general ledger, in individual nominal codes. From the general ledger, you can derive a trial balance that is made up of the sum of all the nominal accounts.
This article will discuss both to help you understand when it might make sense for your company to use double-entry accounting. Double-entry bookkeeping’s financial statements tell small businesses how profitable they are and how financially strong different parts of their business are. You can see how you’ve spent money and how your business is doing. Tthis helps a company make better financial decisions in the future. Small businesses with more than one employee or looking to apply for a loan should also use double-entry bookkeeping.
For businesses using single-entry, you record income and expenses once, hence the name. Outside of simply memorizing the above lists, making debits and credits takes practice.