
(If the asset is still working, the company can keep using it, but it’s done recording the expense.) Amortizable assets get reduced to zero. Depreciable assets get reduced to “salvage value,” which is what the company could expect to get for the asset at the end of its useful life. If there’s no salvage value, then a depreciable asset gets reduced to zero, too. Depreciation is the reduction in value of a tangible asset with the passage of time, usually to account for wear and tear. It spreads the cost of an asset over a specified period of time, typically the asset’s useful life, and is used to match the expense of obtaining an asset to the income that asset helps your business earn. When depreciation expenses appear on an income statement, rather than reducing cash on the balance sheet, they are added to the accumulated depreciation account. Instead of recording the entire cost of an asset on a balance sheet, a business records a portion of an asset’s cost on the income statement in each accounting period for the asset’s lifecycle.

Amortization can demonstrate a decrease in the book value of your assets, which can help to reduce your company’s taxable income. In some cases, failing to include amortization on your balance sheet may constitute fraud, which is why it’s extremely important to stay on top of amortization in accounting.
Depreciation And Amortization: In More Detail
The amount of depreciation to be charged is determined with reference to the useful life of an asset. For example, a vehicle used in the business may be expected to have a useful life of say 5 years, whereas large scale plant and machinery on the other hand may be expected to have a useful life of 10 years or more.
The cost of the building is spread out over its predicted life with a portion of the cost being expensed in each accounting year. Amortization typically uses the straight-line depreciation method to calculate payments. As shown, the total payment for each period remains consistent at $1,113.27 while the interest payment decreases and the principal payment increases. Negative amortization occurs if the payments made do not cover the interest due. The remaining interest owed is added to the outstanding loan balance, making it larger than the original loan amount. Methods for calculating depreciation are Straight Line, Reducing Balance, Annuity, etc.
Do all mortgages have amortization?
Almost all mortgages are fully amortized – meaning the loan balance reaches $0 at the end of the loan term. The exceptions are uncommon loan types, like balloon mortgages (which require a large payment at the end) or interest–only mortgages.
They are considered as long-term or long-living assets as the Company utilizes them for over a year. Intangible AssetsIntangible Assets are the identifiable assets which do not have a physical existence, i.e., you can’t touch them, like goodwill, patents, copyrights, & franchise etc. Tangible assets are recovered over what the IRS calls their “useful life,” which is determined based on the asset type.
Examples Of Depreciation Vs Amortization
If the repayment model for a loan is “fully amortized”, then the last payment pays off all remaining principal and interest on the loan. If the repayment model on a loan is not fully amortized, then the last payment due may be a large balloon payment of all remaining principal and interest. If the borrower lacks the funds or assets to immediately make that payment, or adequate credit to refinance the balance into a new loan, the borrower may end up in default. These deductions often are a difficult concept to grasp because they do not represent a real cash flow and are considered a non-cash transaction, but have real effects on a company’s taxable income. The primary objective of depreciation is to allocate the cost of assets over its expected useful life.
Long term fixed tangible assets mean the assets which are owned by the company for more than three years, and they can be seen & touched. The depreciation is charged as a capital expenditure against the revenue generated from the asset during the year i.e. matching concept. Under units of production method, the annual depreciation charge is computed based on how many units the fixed asset can produce. For example, Robert Inc. buys an asset for $500,000 which is capable of producing 100,000 units during whole of its life.
What is 15 year property depreciation?
Businesses can now treat QIP placed in service after December 31, 2017, as 15-year property. It is eligible for bonus depreciation, allowing taxpayers to deduct up to 100% of the cost of assets that are being depreciated over 39 years under the previous law.
Salvage ValueSalvage value or scrap value is the estimated value of an asset after its useful life is over. For example, if a company’s machinery has a 5-year life and is only valued $5000 at the end of that time, the salvage value is $5000. You can’t depreciate land or equipment used to build capital improvements. You can’t depreciate property used and disposed of within a year, but you may be able to deduct it as a normal business expense.
How Do You Calculate Depreciation And Amortization?
If so, the remaining depreciation or amortization charges will decline, since there is a smaller remaining balance to offset. Both depreciation and amortization are non-cash expenses – that is, the company does not suffer a cash reduction when these expenses are recorded. Interest costs are always highest at the beginning because the outstanding balance or principle outstanding is at its largest amount. It also serves as an incentive for the loan recipient to get the loan paid off in full. As time progresses, more of each payment made goes toward the principal balance of the loan, meaning less and less goes toward interest.
If you want to invest in a publicly-traded company, performing a robust analysis of its income statement can help you determine the company’s financial performance. Amortization Schedule Of LoansLoan amortization schedule refers to the schedule of repayment of the loan. Every installment comprises of principal amount and interest component till the end of the loan term or up to which full amount of loan is paid off.
Company
Patents are typically good for 17 years; if there were 13 years left on this one, you’d amortize the $20,000 over those 13 years. Other potentially amortizable intangible assets include a purchased customer list or a trade name that you acquired when you bought out a competitor and that you plan to eventually phase out.
Tax payers depreciate rental property and business property, including equipment and improvements. The IRS places assets into classes that are each assigned a useful life. That useful life term is the period over which the taxpayer depreciates the cost of the asset. The resulting $7,273 figure is considered a business expense every year for the next 27.5 years. As an expense, it is subtracted from the property income and reduces tax liability. The concept of depreciation arose during the industrialization of the early part of the 19th century. Prior to that time, when a manufacturer had to purchase a significant piece of machinery, the cost was allocated entirely to the year of purchase.
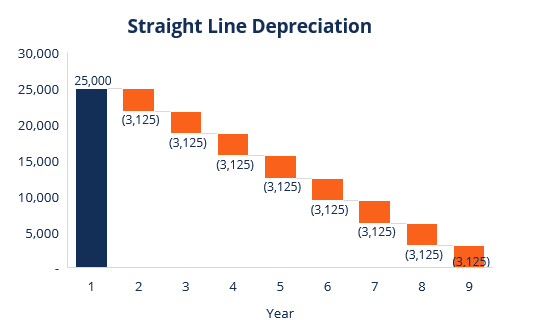
The IRS has set rules about how and when they can deduct depreciation expense. Sometimes the pattern for charging amortization is also given in which the amount is charged every year on a proportionate basis. An organization may opt any method of depreciation, but it should be applied consistently in every financial year. If an organization wants to change the method of depreciation, then the retrospective effect is to be given. Any surplus or deficit arising on account of such change in the method of depreciation shall be debited or credited to the profit & loss account as the case may be. Depreciation can be charged as per several methods including straight line method, reducing balance method and units of production method. This article looks at meaning of and differences between the two different forms of cost allocations of fixed assets – depreciation and amortization.
Does Depreciation Affect Corporate Tax Liability?
A few years ago we as a company were searching for various terms and wanted to know the differences between them. Ever since then, we’ve been tearing up the trails and immersing ourselves in this wonderful hobby of writing about the differences and comparisons. We’ve learned from on-the-ground experience about these terms specially the product comparisons. They both have to be incurred for the successful running of a business cycle. The role played by both in the industry requires knowledgeable auditors and account personnel to work on the numbers. After all, taxation is connected to the government, and producing the right papers for the cost incurred must be legitimate.
They would say that the company should have added the depreciation figures back into the $8,500 in reported earnings and valued the company based on the $10,000 figure. Amount payable on the monthly basis since it does not fully amortize over the term of the loan due to its large amount then it is known as balloon payment.
Intangible assets are non-physical assets that are essential to your business. Customer relationships, contracts, franchises, patents, and licenses amortization definition are all examples of intangible assets—they’re business assets that have no material substance but that add value to your business.
She holds a master’s degree in historic preservation planning from Cornell University. Labor ProductivityLabour productivity is a concept used to measure the worker’s efficiency as the output value produced by a worker per unit of time. By comparing the individual productivity with average, it can be identified whether a particular worker is underperforming or not. This has a been a guide to the top difference between Depreciation vs Amortization. Here we also discuss the Depreciation vs Amortization key differences with infographics, and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.
- Depreciation is an income tax deduction that allows a taxpayer to recover the cost or other basis of certain property.
- Depreciation refers to the reduction in the cost of the tangible fixed assets over its lifespan which is proportionate to the use of the asset in that specific year.
- Intangible Assets are the identifiable assets which do not have a physical existence, i.e., you can’t touch them, like goodwill, patents, copyrights, & franchise etc.
- This is accomplished with an amortization schedule, which itemizes the starting balance of a loan and reduces it via installment payments.
- Instead, the business will depreciate the cost of the car evenly over the course of 15 years.
- For example, Robert Inc. buys an asset for $500,000 which is capable of producing 100,000 units during whole of its life.
Amortization is a measure to calculate the reduced worth of the intangible assets. Depreciation is to be charged as tangible assets suffer wear and tear as they are utilized in the business. Amortization is charged on intangible assets including patents, copyrights, development rights, mailing lists, trademarks, goodwill etc. The amount to be amortized each year depends on the economic or legal life of the intangible asset. For example, a company has obtained a patent costing $1,00,000 which is valid for 20 years. The amount to be amortized each year will be $5,000 (1,00,000/20).
Even in a good business year, the company might show a net loss because it had spent so much on a capital improvement in the same year. Depreciation recognizes that assets have a useful life and wear out over time. When a large piece of equipment is purchased, its cost is evenly divided by the number of years in its useful life.
Can Condo Hoa Fees Be Used As A Capital Loss?
No business can run without owning an asset as the asset generates economic returns and revenue for the business over the life of the asset. It must be depreciated or amortized in the books of accounts to recognize the true value of the asset. Companies use methods like depreciation or amortization to depreciate the asset over its useful life. As an example, suppose in 2010 a business buys $100,000 worth of machinery that is expected to have a useful life of 4 years, after which the machine will become totally worthless . In its income statement for 2010, the business is not allowed to count the entire $100,000 amount as an expense. Instead, only the extent to which the asset loses its value is counted as an expense. The IRS allows businesses to take several accelerated depreciation deductions for tangible business assets and some improvements.
Depreciation
Depreciation refers to the reduction in the cost of the tangible fixed assets over its lifespan which is proportionate to the use of the asset in that specific year. The example of tangible assets which are depreciated is the plant, equipment, machinery, building, and furniture.
The goal in amortizing an asset is to match the expense of acquiring it with the revenue it generates. Amortization is a method of measuring the loss in the value of long-term fixed intangible assets due to the passage of time, to know about their decreased worth is known as amortization. Long term fixed intangible assets are the assets which are owned by the entity for more than three years, but they do not exist in its material form like computer software, license, franchises, etc.