Debits and credit — AccountingTools
What’s On the Balance Sheet?
What is balance sheet definition and meaning?
A balance sheet is a financial statement that reports a company’s assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time, and provides a basis for computing rates of return and evaluating its capital structure.
Liabilities are obligations of the business, like payments you’ve yet to pay, cash you could have borrowed from a bank or buyers. Non current liabilities are principally long term debt of the enterprise.
We now offer eight Certificates of Achievement for Introductory Accounting and Bookkeeping. The certificates embody Debits and Credits, Adjusting Entries, Financial Statements, Balance Sheet, Cash Flow Statement, Working Capital and Liquidity, And Payroll Accounting. A stability sheet is an announcement of the monetary place of a enterprise that lists the assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity at a particular cut-off date. In other phrases, the steadiness sheet illustrates your corporation’s net price.
Liabilities are obligations of the company; they are quantities owed to collectors for a past transaction and so they often have the phrase “payable” of their account title. Along with proprietor’s equity, liabilities can be considered a source of the corporate’s belongings. They can also be considered a claim towards an organization’s assets.
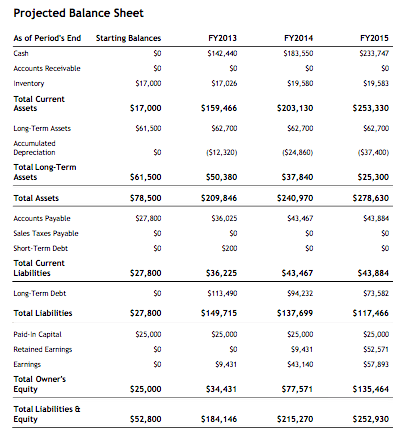
The balance sheet is an invaluable piece of information for traders and analysts; nonetheless, it does have some drawbacks. Since it is just a snapshot in time, it can solely use the difference between this point in time and another single time limit in the past. Your stability sheets show the place of the corporate on a given day, including its total assets, liabilities and equity, which equals its net value. Lenders generally use monetary statements to assess your organization’s creditworthiness. A excessive debt-to-belongings or debt-to-fairness ratio is a concern.
The Balance Sheet is a report of the asset and legal responsibility accounts. Assets are belongings you own in your small business, like cash, capital gear, and money that’s owed to you for services and products you have delivered to customers.
Therefore, a robust steadiness sheet is built on the efficient administration of those major asset types, and a strong portfolio is constructed on knowing the way to read and analyze financial statements. In abstract, the Balance Sheet exhibits the value of all of the capital that a business has built up through the years.
They really must be thought of together as they’re two sides of the identical coin. The major present liabilities are accounts payable and accrued bills. Since we don’t see any accrued expenses on Google’s balance sheet I assume they’re lumping the two together under accounts payable. Both symbolize bills of the business which have but to be paid. The distinction is that accounts payable are for payments the company receives from different companies.
The most essential numbers in it are cash and liabilities. I nearly by no means look at a profit and loss statement without also looking at a balance sheet.
- The Balance Sheet is a report of the asset and liability accounts.
- Assets are things you own in your small business, like money, capital tools, and money that’s owed to you for products and services you’ve delivered to clients.
Some of the essential accounting phrases that you’ll be taught include revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, income assertion, stability sheet, and assertion of money flows. You will turn out to be acquainted with accounting debits and credit as we show you the way to record transactions. You may even see why two fundamental accounting principles, the income recognition principle and the matching precept, guarantee that a company’s income statement stories an organization’s profitability.
If it is very giant in comparison with the total belongings of the enterprise its a cause to be concerned. But its even more necessary to dig into the term of the long run debt and find out when it’s coming due and different essential elements. You’ll have to get the footnotes of the monetary statements to try this. Again, we’ll talk extra about that in a future publish on financial statement evaluation. If not, a journal entry was entered incorrectly, and have to be mounted earlier than monetary statements may be issued.
And accrued expenses are accounting entries a company makes in anticipation of being billed. A good example of an accounts payable is a legal invoice you haven’t paid. A good example of an accrued expense is employee advantages that you haven’t but been billed for that you accrue for each month. The leasing of a sure asset may—on the surface—appear to be a rental of the asset, however in substance it might involve a binding agreement to buy the asset and to finance it via monthly funds. Accountants should look past the form and focus on the substance of the transaction.
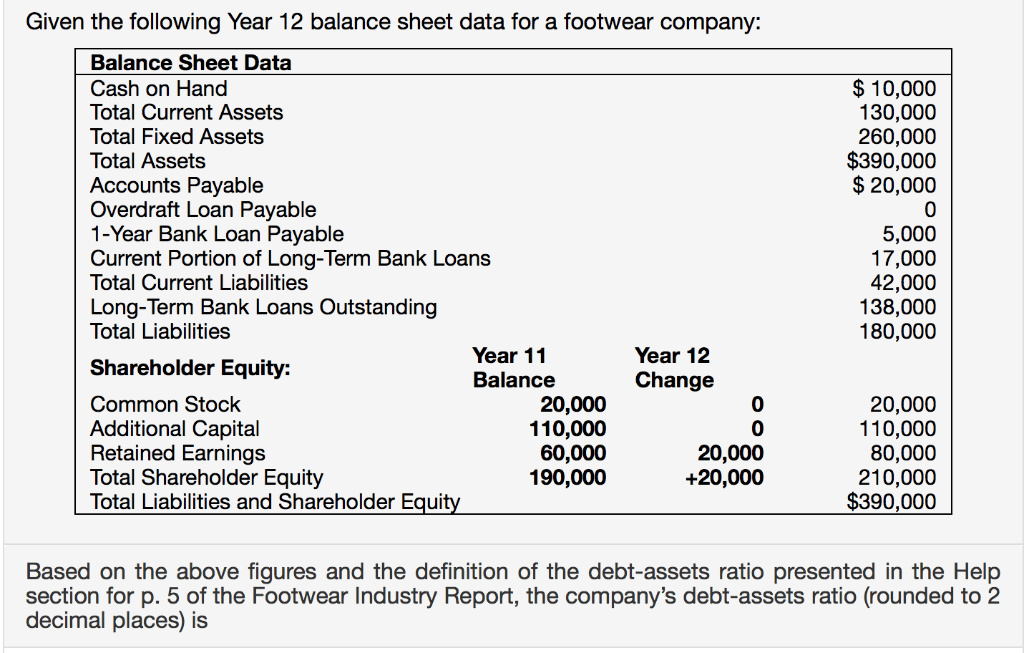
Balance Sheet
For example, an organization’s steadiness sheet reviews property of $100,000 and Accounts Payable of $forty,000 and owner’s equity of $60,000. The supply of the company’s belongings are creditors/suppliers for $40,000 and the homeowners for $60,000. The creditors/suppliers have a declare against the company’s belongings and the owner can declare what remains after the Accounts Payable have been paid. Owners’ equity is mathematically decided to be the difference between your belongings and liabilities.
The purpose of the stability sheet is to disclose the monetary status of a enterprise as of a selected point in time. The statement exhibits what an entity owns (assets) and the way a lot it owes (liabilities), in addition to the amount invested in the business (fairness). This data is more priceless when the steadiness sheets for several consecutive intervals are grouped collectively, so that tendencies in the totally different line objects can be viewed. A number of ratios can be derived from the stability sheet, helping traders get a way of how healthy a company is. These embody the debt-to-fairness ratio and the acid-check ratio, along with many others.
What is a balance sheet used for?
The purpose of the balance sheet is to reveal the financial status of a business as of a specific point in time. The statement shows what an entity owns (assets) and how much it owes (liabilities), as well as the amount invested in the business (equity).
Shareholders’ Equity
The earnings assertion and assertion of cash flows additionally present valuable context for assessing a company’s funds, as do any notes or addenda in an earnings report which may refer again to the stability sheet. It is a monetary assertion that provides a snapshot of what an organization owns and owes, in addition to the quantity invested by shareholders. Assets symbolize objects of worth that a company owns, has in its possession or is due. Of the various forms of items a company owns, receivables, stock, PP&E, and intangibles are usually the 4 largest accounts on the asset aspect of a stability sheet.
In essence, whatever you could have left should you were to promote your whole assets and pay off debt is the worth of the company this present day. Equity really contains a wide range of accounts, but mostly it refers to paid-in capital and retained earnings. Paid-in capital is the par value, or beginning value of your shares if you are a public company. The assets part shows items your organization owns that have tangible value.