
This method of depreciation allows a larger tax deduction in the early years of an asset and less in later years. If you’re wondering what can be depreciated, you can depreciate most types of tangible property such as buildings, equipment vehicles, machinery and furniture. You can also depreciate certain intangible property such as patents, copyrights and computer software, according to the IRS. You generally can’t deduct in one year the entire cost of property you acquired, produced, or improved and placed in service for use either in your trade or business or income-producing activity if the property is a capital expenditure. Depreciation is the recovery of the cost of the property over a number of years.
- Depreciable property can include vehicles, real estate , computers, and office equipment, machinery, and heavy equipment.
- Or you may be required or choose to use a method that spreads deductions for cost over the life of the property.
- The unit of production method is a way of calculating depreciation when the life of an asset is best measured by how much the asset has produced.
- Businesses record this loss of value as depreciation, and there are many ways to measure and record it, according to GAAP and tax purposes.
- Intangible property such as patents, copyrights, computer software can be depreciated.
- Tangible personal property, such as office furniture and heavy machinery.
These depreciation expenses would reduce the asset book value of the equipment and, thus, have a negative impact on equity. PepsiCo Inc. lists land, buildings and improvement, machinery and equipment , and construction-in-progress under its PP&E account. The average useful life for straight-line depreciation for buildings and improvement is years, and 5-15 years for machinery and equipment. In the fiscal year 2017, the company recorded $2.2 billion in depreciated expenses and had $21.9 billion in accumulated depreciation.
What Assets Cannot Be Depreciated?
Straight-line depreciation is the simplest and most often used method. The straight-line depreciation is calculated by dividing the difference between assets cost and its expected salvage value by the number of years for its expected useful life.
Is furniture a depreciable asset?
Defining Furniture, Fixtures and Equipment Real world examples of depreciable assets includes chairs, desks, phones, tables, cabinets, etc., which are used to perform business-related tasks, directly or indirectly.
Gains on dissimilar exchanges are recognized when the transaction occurs. If the truck sells for $15,000 when its net book value is $10,000, a gain of $5,000 occurs.
What Is Depreciation? And How Do You Calculate It?
Qualified improvement property.This is an improvement to the interior portion of a commercial building that has already been placed in service. However, it does not include elevators or escalators, enlargement of the building, or changes in the internal structure of the building. depreciable assets Obsolescence should be considered when determining an asset’s useful life and will affect the calculation of depreciation. For example, a machine capable of producing units for 20 years may be obsolete in six years; therefore, the asset’s useful life is six years.
The group depreciation method is used for depreciating multiple-asset accounts using a similar depreciation method. The assets must be similar in nature and have approximately the same useful lives. There are several methods for calculating depreciation, generally based on either the passage of time or the level of activity of the asset. If an announcement were made after eight years of new technology that caused the item to become obsolete, reporting a $20,000 disposal loss would be appropriate. Any material gains and losses under consideration for reporting should be closely analyzed to determine if they are either the result of improper estimates or current changes in estimated lives or salvage values. In the early days of what is now modern, authoritative GAAP, paras.
Straight-line depreciation, generates a constant expense each year, while accelerated depreciation front-loads the expense in the early years. Subtract the estimated salvage value of the asset from the cost of the asset to get the total depreciable amount. Drafters could include a provision in the partnership agreement that allocates Sec. 179 deductions to nontrust partners and additional other expenses to trust owners.
It is often not an either/or decision in terms of acquiring the right to use an asset. For example, farmers and ranchers generally need both land and equipment in order to produce outputs. The decision usually boils down to how to acquire access to the needed resources or, in the case of expansion, acquiring more of one of them in order to make more efficient use of the existing quantity of the other.
What Kind Of Assets Can You Depreciate?
Under this method, the annual depreciation is determined by multiplying the depreciable cost by a schedule of fractions. Does not include assets used in mining, assets used in the manufacture of primary ferrous and nonferrous metals, assets included in class 00.11 through 00.4 and assets elsewhere classified. If an asset is sold for cash, the amount of cash received is compared to the asset’s net book value to determine whether a gain or loss has occurred.
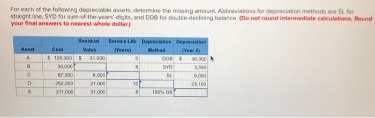
A fixed asset is an asset purchased by a company that has a useful life of more than a single accounting period and is to be used for productive purposes within the business. Property described in asset class 00.12 which is qualified technological equipment as defined in section 168 is assigned a recovery period of 5 years notwithstanding its class life. Because business assets such as computers, copy machines and other equipment wear out, you are allowed to write off (or “depreciate”) part of the cost of those assets over a period of time. These tips offer guidelines on depreciating small business assets for the best tax advantage. Depreciable business assets include most forms of property, including buildings, machinery, vehicles, furniture, and computers. You can also depreciate some forms ofintangible property like patents, copyrights, and computer software. Another complicating element is the fact that often these investments are not equal in value.
Our continued learning packages will teach you how to better use the tools you already own, while earning CPE credit. 48.31TOCSC-Electric Power Generating & Distribution SystemsIncludes assets used in the provision of electric power by generation, modulation, rectification, channelization, control, and distribution. Does not include these assets when they are installed on customers premises. Telephone Communications noteIncludes the assets identified below and that are used in the provision of commercial and contract telephonic services. Try our solution finder tool for a tailored set of products and services.
Ratepayers also pay for carrying costs such as maintenance, taxes, insurance, administrative costs and interest expense for the asset. So, if you use an accelerated depreciation method, then sell the property at a profit, the IRS makes an adjustment. They take the amount you’ve written off using the accelerated depreciation method, compare it to the straight-line method, and treat the difference as taxable income. Depreciation calculations require a lot of record-keeping if done for each asset a business owns, especially if assets are added to after they are acquired, or partially disposed of. However, many tax systems permit all assets of a similar type acquired in the same year to be combined in a “pool”. Depreciation is then computed for all assets in the pool as a single calculation. These calculations must make assumptions about the date of acquisition.
(Other members of your family do not use this computer.) Therefore, you can depreciate 2/3 of the cost of the computer. A business will frequently acquire both land and an office building. In these cases, only the portion of the price that is attributed to the building is depreciable. If you acquire property by gift, your depreciable basis is same as the donor’s basis at the time of the gift. Section 1250 is only relevant if you depreciate the value of a rental property using an accelerated method, and then sell the property at a profit. For example, let’s say the assessed real estate tax value for your property is $100,000. The assessed value of the house is $75,000, and the value of the land is $25,000.
How Is Computer Software Classified As An Asset?
Instead, you’ll have to use the actual formulas on which the tables are based. Consult your tax adviser or the IRS’s free Publication 946, How to Depreciate Property, for details on how this is done. Once you’ve claimed some depreciation on a piece of business property, the depreciation is deducted from the cost to arrive at the adjusted basis. It’s important that you keep capital asset records that include the amount of accumulated depreciation you’ve claimed for each asset over the years, so you can easily compute the adjusted basis when the need arises.
It may look like a smaller commitment with lower risk but it is also a commitment to depreciation expense that introduces risk to the operation. Normally, a business reduces the depreciable basis of the assets by the full amount of the Sec. 179 deduction taken. However, because the deduction allocated to the estate or trust otherwise would provide no tax benefit, Regs. The units-of-production method is calculated based on the units produced in the accounting period. Depreciation expense will be lower or higher and have a greater or lesser effect on revenues and assets based on the units produced in the period.
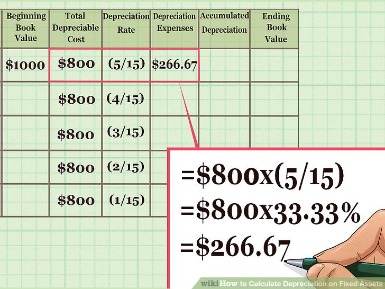
As a reminder, it’s a $10,000 asset, with a $500 salvage value, the recovery period is 10 years, and you can expect to get 100,000 hours of use out of it. In the case of intangible assets, the act of depreciation is called amortization. For example, the IRS might require that a piece of computer equipment be depreciated for five years, but if you know it will be useless in three years, you can depreciate the equipment over a shorter time. Assets you’re placing in service this year might also be eligible for bonus depreciation or the section 179 deduction. The straight line method, which spreads expenses evenly across an asset’s depreciable life. Of course, there are many software programs out there that will not only help you track your organizations assets but will also calculate depreciation and produce reports for you. Regardless, we recommend that all organizations have guidelines in place for how they plan to estimate useful life.
How Do You Know If Something Is A Noncurrent Asset?
Generally, if you’re depreciating property you placed in service before 1987, you must use the Accelerated Cost Recovery System or the same method you used in the past. For property placed in service after 1986, you generally must use the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System . Business assets that deteriorate over time but last at least one year usually qualify for depreciation. While buying power changes over time as the result of inflation and deflation, cash itself maintains the same value. A $20 bill will always be worth $20, even when $20 doesn’t buy as much as it used to. You stop depreciating a business asset when either one of two events occur. Second, that asset could reach the end of its useful life—then it is no longer is being depreciated.
This has the effect of converting from declining-balance depreciation to straight-line depreciation at a midpoint in the asset’s life. The double-declining-balance method is also a better representation of how vehicles depreciate and can more accurately match cost with benefit from asset use. The company in the future may want to allocate as little depreciation expenses as possible to help with additional expenses. The most common types of depreciation methods include straight-line, double declining balance, units of production, and sum of years digits. This method of depreciation is tied more closely to the property’s usage or production capacity than the passage of time.

For real estate, you can also include costs of legal and accounting fees, revenue stamps, recording fees, title abstracts/insurance, surveys, and real estate taxes assumed for the seller. Remember you can only depreciate the buildings—land is never depreciable. The depreciable basis is equal to the asset’s purchase price, minus any discounts, and plus any sales taxes, delivery charges, and installation fees. Costs of assets consumed in producing goods are treated as cost of goods sold.
How Is Depreciation Calculated?
With this system in place, you select the most appropriate depreciation method and convention for calculating depreciation on an item. The most common of these is the General Depreciation System , which contains the recovery periods referenced above. However, you may be required by law to use the Alternative Depreciation System , which has different recovery periods. Property life can range from five years to 39 years for commercial buildings. Depreciation expense under units-of-production, based on units produced in the period, will be lower or higher and have a greater or lesser effect on revenues and assets. The effect of the straight-line method is a stable and uniform reduction in revenues and asset values in every accounting period of the asset’s useful life.
Depreciation is a process of deducting the cost of an asset over its useful life. Assets are sorted into different classes and each has its own useful life. Depreciation is technically a method of allocation, not valuation, even though it determines the value placed on the asset in the balance sheet.
Bonus depreciation has been changed for qualified assets acquired and placed in service after September 27, 2017. The old rules of 50% bonus depreciation still apply for qualified assets acquired before September 28, 2017.
The choice of depreciation method can impact revenues on the income statement and assets on the balance sheet. Under MACRS, the capitalized cost of tangible property is recovered by annual deductions for depreciation over a specified life. The lives are specified in the Internal Revenue Service’s Tax Co de. The deduction for depreciation is computed under one of two methods at the election of the taxpayer. To calculate depreciation using the double-declining method, its possible to double the amount of depreciation expense under the straight-line method.