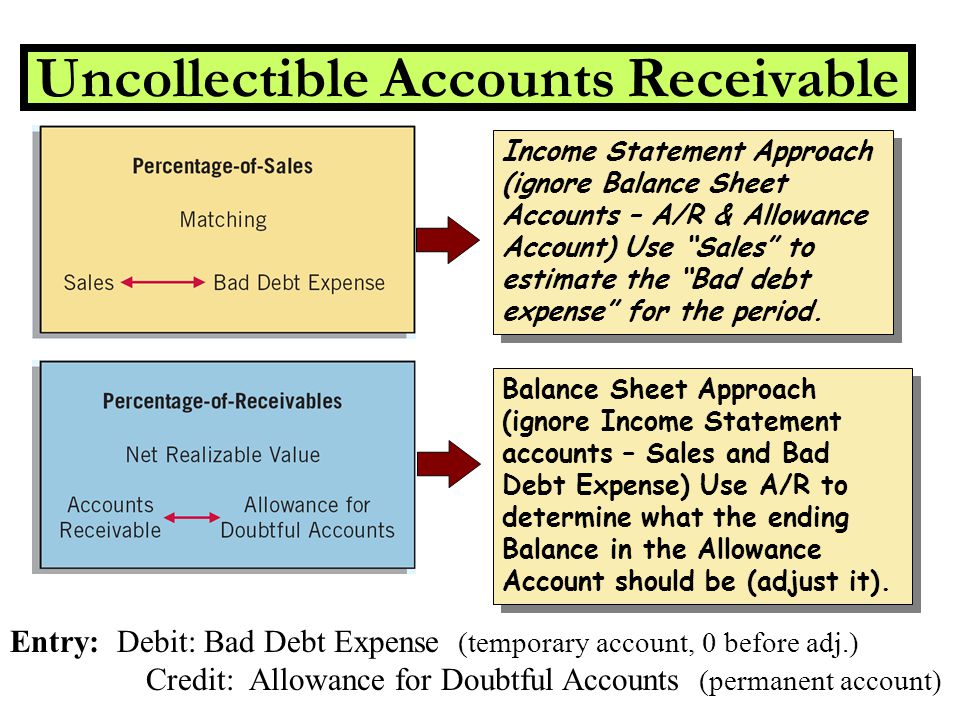
Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts
The uncollectible accounts expense account exhibits the corporate estimates it price $750 in January to sell to clients who is not going to pay. The accounts receivable account exhibits the company’s clients owe it $50,000. The allowance for uncollectible accounts exhibits the corporate expects its clients to be unable to pay $750 of the $50,000 they owe. Based on accounts receivable and the allowance for uncollectible accounts, the company would predict it could collect $forty nine,250 ($50,000 – $750) from its credit prospects.
When an organization estimates that some of its accounts receivable are uncollectible, in impact it’s saying some of its accounts receivable are not assets. Similarly, it’s saying its sources of assets are too excessive as a result of some credit gross sales will never result in resources, particularly money. Remember, accounts receivable usually are not priceless if they do not eventually end in cash. In order to correctly account for uncollectible accounts receivable, firms reduce their assets and sources of assets for estimated uncollectible accounts receivable. For instance, if a company with $50,000 of January credit score gross sales estimates that 1.5% of such gross sales will not be collected, it will be affected as follows.
Allowance for uncollectible accounts is a contra asset account on the stability sheet representing accounts receivable the company doesn’t expect to collect. When prospects buy products on credit score and then don’t pay their bills, the selling company should write-off the unpaid bill as uncollectible.
For example, if the company had January credit sales of $15,000, it might estimate its uncollectible accounts receivable to be $210 ($15,000 x .014). The .014 is the average percentage of uncollectible accounts receivable during 12 months 1 through 12 months three. On the other hand, since that information suggest uncollectible accounts are growing, from 1.25% in 12 months 1 to 1.fifty five% in 12 months 3, the company might estimate its uncollectible accounts receivable to be $255 ($15,000 x .017). The .017 reflects an expected enhance in uncollectible accounts receivable from the 1.fifty five% experienced in year three.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts: Calculation
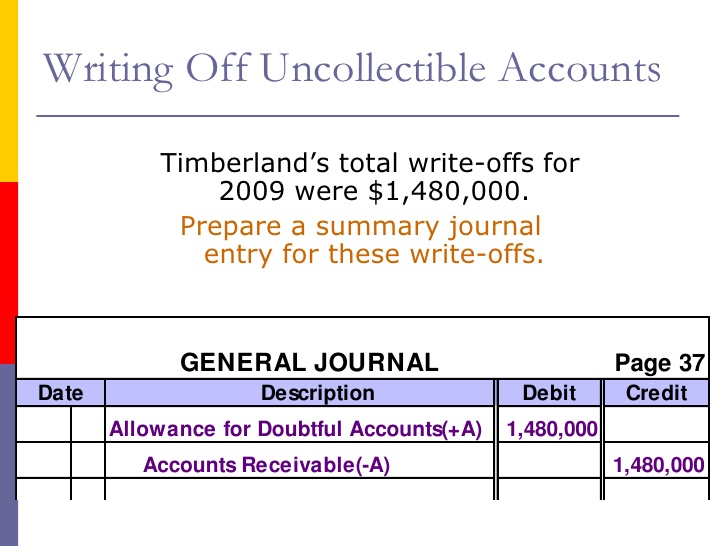
The mixture balance within the allowance for uncertain accounts after these two durations is $5,400. As a outcome, its November revenue statement will be matching $2,four hundred of unhealthy money owed expense with the credit gross sales of $800,000. If the balance in Accounts Receivable is $800,000 as of November 30, the company will report Accounts Receivable (web) of $797,600. When credit sales are made, the effect is a rise in assets (assets) and an increase in sources of assets (stockholders equity). The particular accounts affected are accounts receivable (debited) and gross sales (credited).
Regardless of which percentage is used, both percentage would in all probability end in a reasonable estimate of uncollectible accounts receivable. Using the 1.70% estimate, the Nicholas Corporation would put together the following journal entry to record uncollectible accounts expense in January.
The provision for doubtful money owed is the estimated amount of unhealthy debt that will arise from accounts receivable that have been issued but not yet collected. Thus, the net impression of the availability for doubtful money owed is to accelerate the popularity of dangerous money owed into earlier reporting durations. The Nicholas Corporation might use the above information to estimate its uncollectible accounts receivable in yr 4.
Allowance for uncollectible accounts can also be referred to as allowance for uncertain accounts, and may be expensed as bad debt expense or uncollectible accounts expense. The provision for bad debts could discuss with the steadiness sheet account also known as the Allowance for Bad Debts, Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, or Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts. If so, the account Provision for Bad Debts is a contra asset account (an asset account with a credit steadiness). It is used together with the account Accounts Receivable to ensure that the steadiness sheet to report the online realizable worth of the company’s accounts receivable. The entry to extend the credit stability in these contra accounts is a debit to the revenue statement account Bad Debts Expense.
Adjusted Trial Balance
- Allowance for uncollectible accounts is a contra asset account on the stability sheet representing accounts receivable the company does not anticipate to collect.
- Allowance for uncollectible accounts is also referred to as allowance for doubtful accounts, and may be expensed as bad debt expense or uncollectible accounts expense.
- When clients purchase merchandise on credit and then don’t pay their bills, the selling company should write-off the unpaid invoice as uncollectible.
This information of anticipated money collections is very important for managers who should plan their money expenditures. Even though its prospects owe it $50,000, administration wouldn’t plan on spending the total $50,000 because $750 will in all probability by no means be acquired. Uncollectible accounts expense was debited within the above journal entry to be able to acknowledge the expense of promoting to some prospects who will not pay.
One Response to Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts
Since bills lower stockholders fairness, and stockholders equity decreases with debits, uncollectible accounts expense was debited. The allowance for uncollectible accounts was credited as a result of the corporate’s (resources) decreased. Inasmuch as it usually has a credit stability, versus most belongings with debit balances, the allowance for uncollectible accounts is known as a contra asset account. The sales technique applies a flat share to the entire greenback amount of gross sales for the period. For example, based on earlier experience, a company might anticipate that 3% of web gross sales aren’t collectible.
How do you calculate allowance for uncollectible accounts?
Allowance for uncollectible accounts is a contra asset account on the balance sheet representing accounts receivable the company does not expect to collect. When customers buy products on credit and then don’t pay their bills, the selling company must write-off the unpaid bill as uncollectible.
AccountingTools
It is important to note why firms use the allowance for uncollectible accounts somewhat than simply using accounts receivable. At the time uncollectible accounts expense is estimated, accounts receivable can not be decreased instantly as a result of the specific customers who will not pay usually are not recognized at that time. Since the specific prospects are not recognized, customer accounts within the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger can not be decreased.
The entry will contain the working expense account Bad Debts Expense and the contra-asset account Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. Later, when a selected account receivable is definitely written off as uncollectible, the corporate debits Allowance for Doubtful Accounts and credit Accounts Receivable. The percentage of credit score sales approach focuses on the income assertion and the matching principle. Sales revenues of $500,000 are instantly matched with $1,500 of unhealthy money owed expense.
Thus, for the reason that accounts receivable subsidiary ledger can’t be reduced, accounts receivable in the general ledger can not be reduced or the two ledgers wouldn’t lend a hand. Remember the total of all accounts in the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger equals the steadiness in accounts receivable within the general ledger. Both the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger and the accounts receivable account within the general ledger will be lowered when the company identifies the specific prospects who is not going to pay. Under the allowance technique, a company records an adjusting entry on the end of every accounting period for the amount of the losses it anticipates as the results of extending credit to its prospects.
Understanding the Allowance For Doubtful Accounts
If the total net sales for the period is $a hundred,000, the corporate establishes an allowance for doubtful accounts for $3,000 whereas simultaneously reporting $three,000 in dangerous debt expense. If the next accounting interval ends in internet sales of $80,000, an additional $2,four hundred is reported within the allowance for uncertain accounts, and $2,four hundred is recorded within the second interval in bad debt expense.
The balance in the account Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is ignored at the time of the weekly entries. However, at some later date, the stability in the allowance account have to be reviewed and perhaps further adjusted, so that the stability sheet will report the right internet realizable value. If the seller is a new company, it might calculate its bad money owed expense through the use of an business average until it develops its own expertise rate.